Deploying VRO Part 1: Deploying VRO
Introduction
As many organizations reevaluate their reliance on VMware, the need for platform-agnostic disaster recovery becomes critical. Whether due to licensing changes, cost pressures, or strategic shifts, the trend toward mobility is accelerating.
This blog series explores how Veeam Recovery Orchestrator (VRO) 7.2.1 can play a key role in disaster recovery planning and execution.
In Part 1, we’ll walk through the deployment of VRO, setting the stage for Hyper-V integration in Part 2 and a Hyper-V-based Restore scenario in Part 3.
The Process at a Glance
1. Prerequisites
Ensure the following are in place:
- Veeam Backup & Replication (VBR) v12.1 or later
- A dedicated Windows Server for the VRO installation
- SQL Server (local or remote)
- Network access to your Hyper-V hosts and VBR server
- A service account with administrative rights and required access
2. Deployment Steps
-
Download the Installer
Download the VRO 7.2.1 installer from the Veeam website or your customer portal. -
Run the Setup
On your VRO server, launch the installer and select:- Veeam Recovery Orchestrator Server

- Accept the license agreement
- Install all the required components
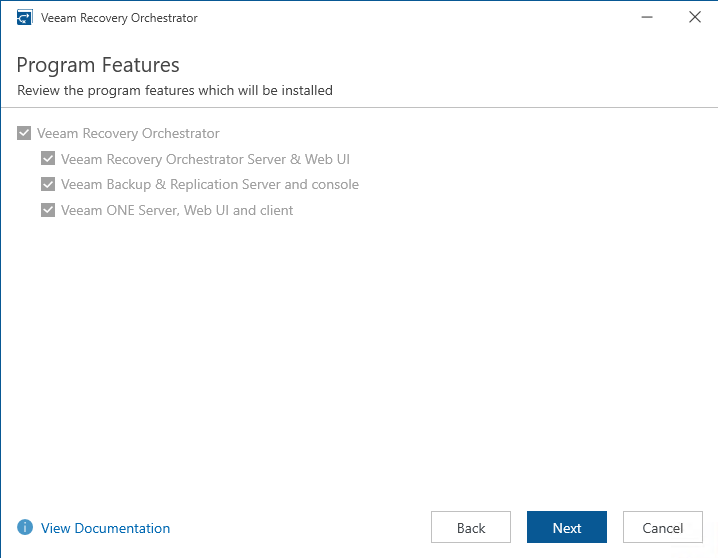
- Provide a valid license file
- Specify the service account details
At this point, the installer will run a system configuration check to ensure all required features are enabled.
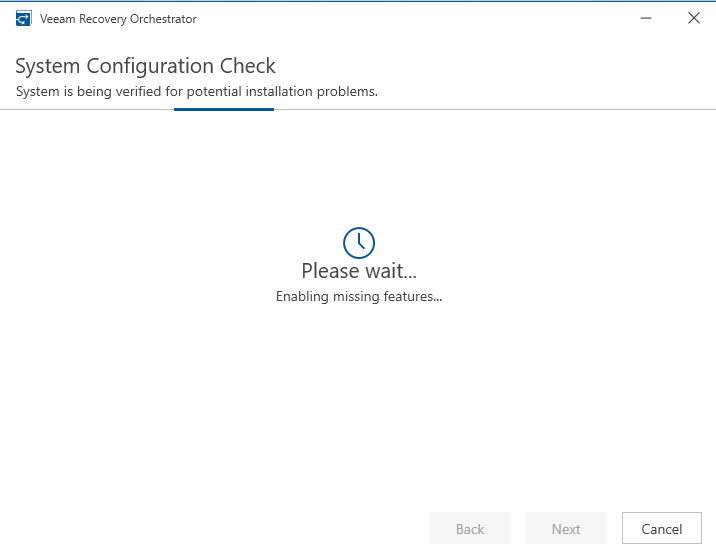
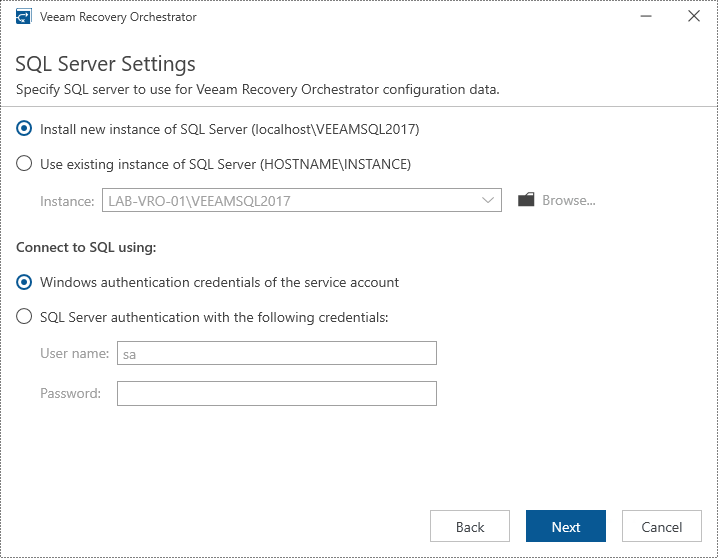
- Configure SQL Server connection:
- If using an external SQL server, specify the connection details
- Provide database name and credentials
- Choose the installation location
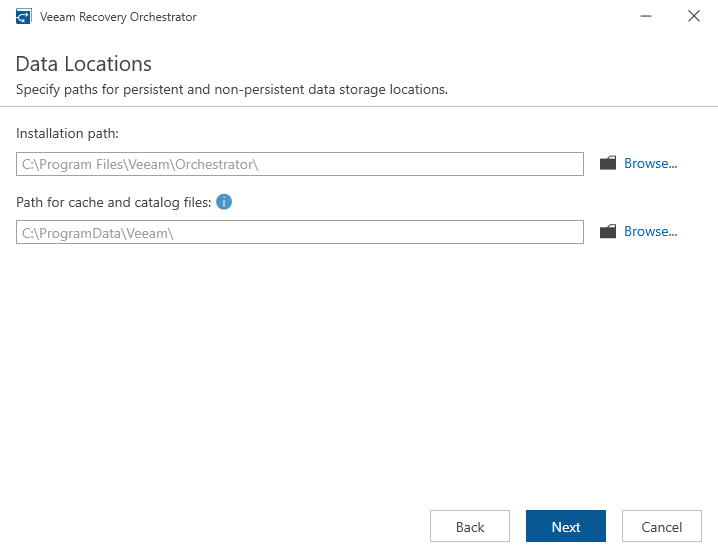
- Confirm or configure the required ports
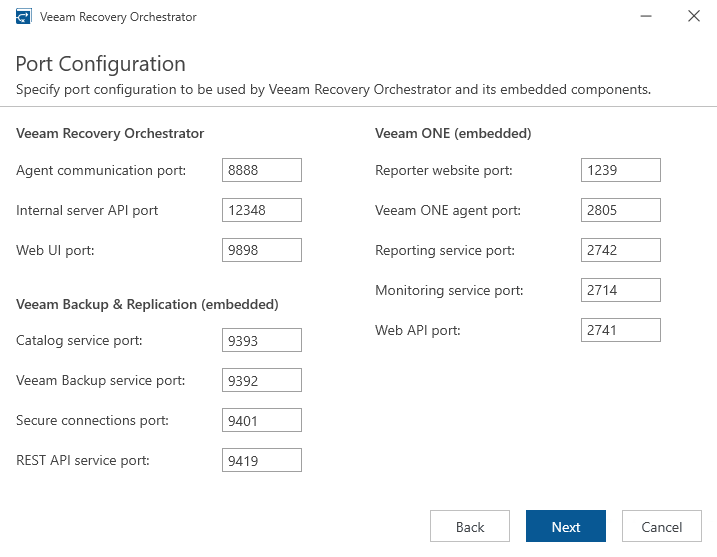
- Generate a new security certificate
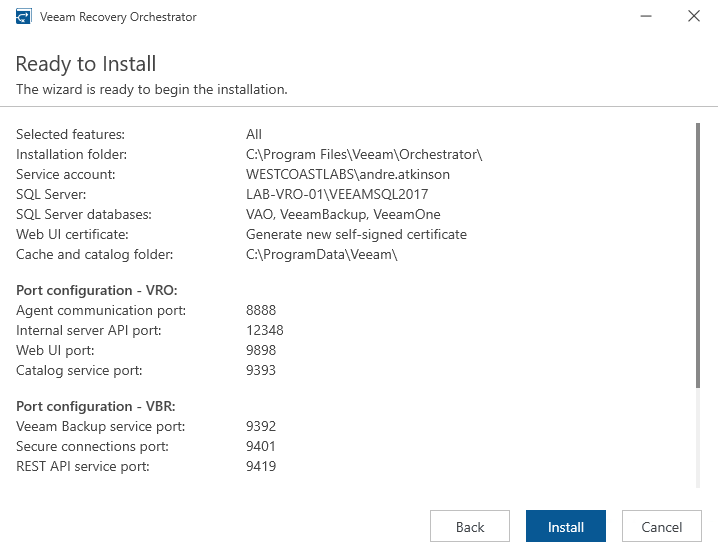
- Finalize the installation and click Install
🔄 In Part 2, we’ll map Hyper-V hosts and begin configuring the actual failover targets — the real meat of moving off VMware.
Conclusion
Deploying VRO is a strategic first step toward platform-independent disaster recovery. For organizations looking to move away from VMware, it allows you to build DR workflows that work today with VMware but are future-ready for Hyper-V — and even cloud.
In Part 2, we’ll configure Hyper-V integration, define recovery locations, and show how to prep workloads for cross-hypervisor mobility.